How to Pay Back Student Loans
To pay for student loans, you need a great repayment strategy covering almost every aspect of managing your finances.
This will ensure you’ll not keep getting another loan just to cover up your student loans, which can bury you in debt.

You see, paying back student loans can seem daunting, but with a proper understanding of your loans and a solid repayment strategy, it can be much more manageable than you might think.
In fact, there are government efforts to help people ease off their student loans, which include multiple programs, like PSLF, AOTC, and LLC (more of these later on this blog).
Also, President Biden attempted to help more than 43 million borrowers with their piling up student loan debt, but the Supreme Court rejected it.
Why? Well, maybe because with the number of people having student loans, it’s just impossible, and unfair, for the administration to put the burden of paying those loans on the taxpayers.
So, what’s the best course of action now?
It’s knowing everything about student loan debt and creating a great repayment plan, which includes effectively managing your finances.
That said, with my expertise in student loans, I’ll guide you through the process of understanding your loans, creating a repayment strategy, accelerating repayment, and managing financial challenges.
I’ll include additional tips and resources as well.
Understanding Your Student Loans
Before you dive into the repayment strategies for repaying your student loan, you must first understand (not just know) the different student loans one can get.
Let’s get back to the basics first.
Types of Student Loans
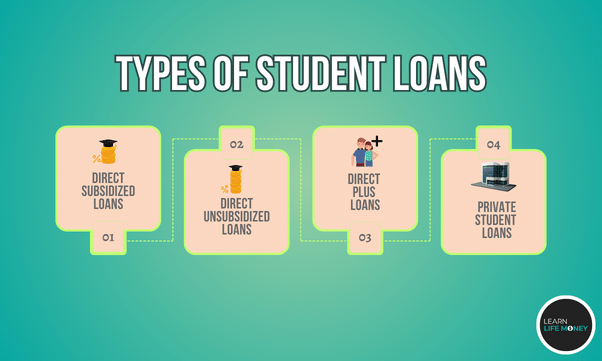
The types of student loans majorly fall into government-supported and private loans.
Government-supported loans, commonly known as federal loans, have different types and features tailored to various needs.
The most known are:
- Direct Subsidized Loans. Specifically designed for students with demonstrated financial need, these loans have favorable terms as the government pays the interest during certain periods.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans. Unlike subsidized loans, these are not based on financial need and are available to all eligible students. However, the borrower is responsible for all interest.
- Direct PLUS Loans. These loans are meant for graduate or professional students, including parents of dependent undergraduate students. Of course, the borrower is fully responsible for all interest.
On the other hand, financial institutions also offer support to the educational journey through a private student loan.
Private student loans mostly fill the gap when federal loans, scholarships, and other financial aid are insufficient.
The issuing financial body determines the terms and conditions of such a private student loan.
Keep in mind that these descriptions are for general guidance only; do your research and consider your financial situation carefully when choosing a loan type or loan servicer.
Loan Terms and Conditions

One of the first key steps to achieving financial literacy in your educational journey is getting to grips with the terms and conditions of any loan you consider or take from any loan servicer or provider.
Whether it’s a federal or private loan, the details in the fine print could make a significant difference in handling loan repayments properly.
Start by understanding the basic terms; principal, interest rate, repayment period, grace period, etc.
Remember, the principal is the initial amount you borrow, whereas the interest rate is what the lender charges for borrowing their money.
Next, pay close attention to the interest rates a loan servicer gives.
While some loans have fixed interest rates, others have variable rates, which can change over time.
Fixed interest rates remain consistent throughout the loan’s life, making budgeting for payments easier.
Variable interest rates, on the other hand, might start lower but can increase, potentially making your loan more costly over time.
Finally, read and understand the terms of repayment.
Check the grace period, which is the time you’re permitted to start making payments after leaving school.
Also, check if there are pre-payment penalties or benefits for consistent on-time payments.
Knowing these details will prevent unpleasant surprises in the future.
Tracking Your Student Loan
Now that you’ve explored the terms and conditions given to you by a loan servicer, it’s crucial to make a plan for tracking your loans.
Monitoring helps keep a clear understanding of your loan balance, the amount you’ve paid, outstanding amounts, and when payments are due.
One helpful tool for tracking federal student loans is the National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS).
This is the U.S. Department of Education’s central database for federal student aid and provides a centralized view of your federal loans.
If you also have private loans, consider using budgeting tools or apps to track multiple types of loans in one place. This can be particularly helpful if you have loans from various lenders.
Knowing where you stand can motivate you to take the necessary steps to pay off student loans faster.
Remember, ignorance is not bliss when dealing with student loans!
Creating a Repayment Strategy

Entering the world with a student loan can seem imposing, but with the correct strategy, it doesn’t have to be.
Establishing a Budget
The initial phase in creating a repayment plan is establishing a realistic budget.
Start by determining your fixed monthly expenses, such as rent, utilities, groceries, and, importantly, your student loan payments.
Next, allow for variable expenses like entertainment, clothing, traveling, etc.
Now, balance your income against your expenses.
The goal is to ensure that your income covers your expenses and leaves some margin for savings and emergencies.
If your student loan payments are too high to allow for such savings, you may need to adjust other areas of your spending or consider different repayment plans.
Many fall into a student loan debt cycle due to not knowing how to establish a budget properly (seriously, you need to think of budgeting thoroughly).
Choosing a Repayment Plan
Once you have a realistic budget, it’s time to choose a repayment plan that fits.
For federal student loans, there are several repayment options.
The standard 10-year repayment plan is the most common and involves fixed payments over a decade.
However, if your monthly budget can’t accommodate the standard plan, there are income-driven repayment plans.
These base your monthly payments on your income and family size and can make payments more manageable.
If you have private student loans, your repayment options will be determined by the specific lender.
Ensure to communicate with your lender about possible repayment plans if you’re struggling to meet your regular payments.
Consolidating or Refinancing Your Loans
It’s worth considering a direct consolidation loan or refinancing your loans to make repayment more manageable.
Federal student loan consolidation combines all of your federal loans into one, which could simplify repayment.
However, it might result in a slightly higher interest rate because it is averaged across your loans.
If that’s not to your liking, you can go for the refinancing option. It involves taking a new loan with a private lender to pay off student loans, which could help if you have high-interest private loans.
Remember, good credit will enable you to secure a lower interest rate, which could save significant money over the course of repayment.
However, remember that refinancing federal student loans with private lenders means giving up federal loan benefits, including access to income-driven repayment plans.
Accelerating Loan Repayment
Once you’ve established a repayment strategy, you may be eager to accelerate your loan repayment and free yourself from debt even sooner.
Increasing Your Monthly Payments
If you find yourself in a better financial situation, consider making a larger monthly payment to pay off student loans faster.
By contributing more than the minimum monthly payment required, you’ll reduce the principal amount and overall interest faster.
This tactic may also shorten the loan term and help you save money in the long run.
Remember, though, that this might not be applicable for fixed terms.
For private student loans, make sure to inform your lender that you would like the extra payment to be applied to the principal balance and not future payments.
Applying for Student Loan Forgiveness Programs

You might qualify for student loan forgiveness programs depending on your career choice and other factors.
For federal student loans, Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) is a popular option, which forgives any remaining loan balance after ten years of consistent payments for public service employees.
Additionally, federal loan borrowers in specific professions such as teaching, nursing, and law may be eligible for specific forgiveness programs.
Just investigate loan forgiveness opportunities relevant to your situation, as they can be a significant boost in eliminating your loan burden.
Utilizing Employer Student Loan Assistance Programs
Some employers offer to help their employees pay off student loans.
This benefit often involves direct contributions from the employer toward your loan repayment, reducing the overall balance and shortening repayment time.
To take advantage of this, inquire with your organization’s human resources department to see if such programs are available.
Tax Deductions and Credits
Be mindful of tax deductions and credits related to student loan interest.
The U.S. federal government allows eligible borrowers to take away up to $2,500 in student loan interest from their yearly taxable income.
Moreover, education-related tax credits like the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) and the Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) can help ease the overall tax burden, freeing up funds you can use to pay down your student loans.
Managing Financial Challenges

It’s also important to be prepared for unforeseen financial challenges that you might face over the course of your repayment journey.
Deferment and Forbearance Options
If you’re facing temporary hardship and are unable to make a consistent monthly payment, consider applying for deferment or forbearance.
These options allow you to pause or reduce your loan payments temporarily.
While interest usually continues to accrue during these periods, this can provide necessary breathing room in times of financial strain.
However, the criteria for eligibility vary, so ensure to communicate with your lender about these options.
Identifying and Avoiding Student Loan Scams

Unfortunately, student loan scams are increasingly common.
These scammers prey on borrowers by promising instant loan forgiveness or drastically lowered payments in exchange for high upfront fees.
Always remember, legitimate student loan servicers will never ask for fees upfront.
To avoid scams, work only with established, reputable institutions, and always be skeptical of offers that seem too good to be true.
Dealing With Delinquency and Default
If you miss a loan repayment, your loan becomes delinquent.
And if the delinquency continues, you may eventually default on your loan, which can have severe financial consequences.
But if you’re struggling to make your payments, contacting your lender as soon as possible is essential.
They can work with you to find a solution, such as changing your repayment plan, that can help avoid delinquency or default.
Additional Tips and Resources
Here are a few extra resources that can support your repayment journey.
Seeking Professional Financial Advice

Sometimes, managing student loans and other financial obligations can feel overwhelming.
A trained financial advisor can provide guidance tailor-fit to your circumstances, assisting you in creating a plan that best suits your financial capabilities and goals.
Leveraging Online Tools and Apps
From student loan repayment calculators to budgeting apps, there are many digital tools designed to simplify money management.
Some of them are the following in no particular order:
Staying Informed and Adapting Your Strategy

Financial situations can change, and so can government policies related to student loans.
Stay informed about changes that might affect your student loans, and be ready to adjust your student loan repayment strategy accordingly.

Final Thoughts on How to Pay Back Student Loans
As you can see, navigating through student loan repayment may be a complex process filled with terminology, paperwork, and important decisions.
However, with clear information and careful strategy, you can manage your loans effectively and move toward your financial goals.
Remember that you’re not alone on this journey; hundreds of resources are available to guide you, and your persistence will reward you in the long run.


















